CULTURESCAPE DATASETS:
Sitescape Communography Classometry Povertyscape YARD Chronos Paideia Competenza Skillability Religidox
DATA ANALYTICS: Econometrics Identitate Culturescape Geodemographics
Overview of Paideia: Adult Literacy Skills
For the ancient Greeks, paideia referred to the education and socialization of the population into model citizens. Paideia training included practical, scientific, and moral education to produce a well-rounded individual.
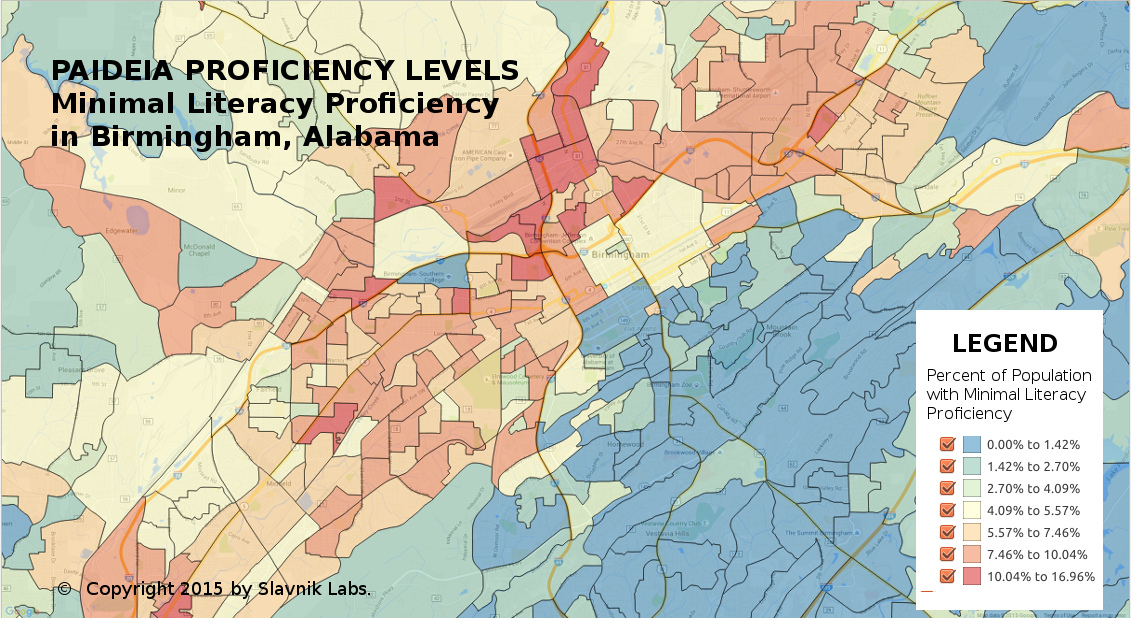
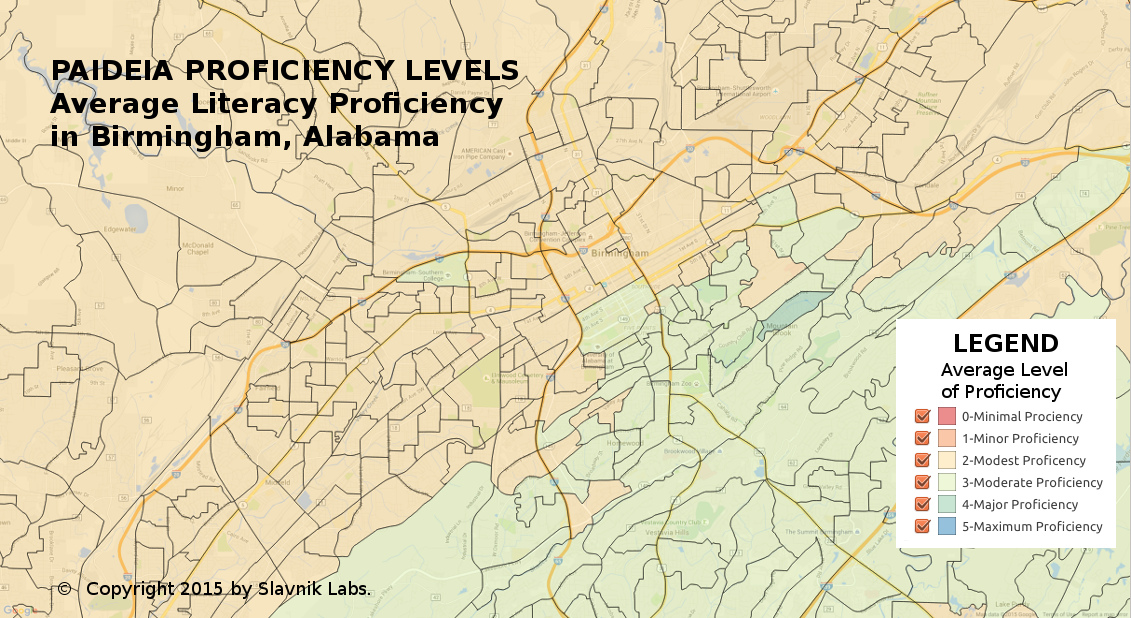
The PAIDEIA dataset provides current year proficiency assessments of adult competencies for more than 300 variables, although the key scores revolve around literacy, numeracy, and problem solving skills. The PAIDEIA dataset was created by applying sophisticated statistical techniques to the Program for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies (PIAAC) released by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) of the US Department of Education. The PIAAC is "a household study conducted under the auspices of the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) to assess key cognitive and workplace skills needed for successful participation in 21st century society and the global economy."
The PAIDEIA dataset delivers reliable estimates of literacy, numeracy, and problem solving scores. In addition, the dataset gives estimates for variables related to educational activities, employment, skills used at work and skills used in everyday life. Our documentation gives additional data about the PAIDEIA dataset together with a methodological summary. The dataset has been grouped by 6 proficiency levels.